Magnesium is one of those essential minerals that doesn’t always get the spotlight it deserves, yet it plays a critical role in nearly every system in your body. From supporting muscle function to boosting brain health, magnesium is a true multitasker. Despite its importance, many people don’t get enough of this vital nutrient, leading to a range of health issues.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the benefits of magnesium, the causes of deficiency, and the best ways to ensure you’re getting enough of it.
Why Magnesium Matters: Key Benefits
Magnesium is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, making it essential for overall health. Here are some of the most significant benefits of magnesium:
1. Supports Heart Health
Magnesium is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. It helps regulate blood pressure, supports normal heart rhythm, and relaxes blood vessels, improving circulation. Studies have shown that adequate magnesium intake can reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes.
2. Boosts Brain Function and Mood
Magnesium plays a key role in brain health by regulating neurotransmitters, which send messages throughout the brain and nervous system. It has been linked to improved memory, focus, and even mood regulation. Some research suggests that magnesium may help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
3. Promotes Muscle Relaxation and Recovery
If you’ve ever experienced muscle cramps or spasms, a magnesium deficiency could be to blame. Magnesium helps muscles relax and contract properly, making it essential for athletes and anyone with an active lifestyle. It also aids in post-workout recovery by reducing inflammation and soreness.
4. Strengthens Bones
While calcium often steals the spotlight for bone health, magnesium is just as important. It helps convert vitamin D into its active form, which is necessary for calcium absorption. Without enough magnesium, your bones may become weak and brittle over time.
5. Regulates Blood Sugar Levels
Magnesium plays a role in insulin sensitivity, helping to regulate blood sugar levels. This is particularly important for people with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Studies have shown that higher magnesium intake is associated with a lower risk of diabetes.
6. Improves Sleep Quality
Struggling with insomnia or restless nights? Magnesium may help. It regulates the production of melatonin, the hormone responsible for sleep, and calms the nervous system, promoting relaxation and better sleep quality.
Causes of Magnesium Deficiency
Despite its importance, magnesium deficiency is surprisingly common. Here are some of the leading causes:
1. Poor Diet
A diet high in processed foods and low in whole, nutrient-dense foods is a major contributor to magnesium deficiency. Refined grains, sugary snacks, and fast food often lack essential minerals like magnesium.
2. Soil Depletion
Modern farming practices have led to soil depletion, reducing the magnesium content in many crops. Even if you’re eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, they may not contain as much magnesium as they once did.
3. Chronic Stress
Stress depletes magnesium levels in the body, creating a vicious cycle. Low magnesium can make you more susceptible to stress, and stress further reduces magnesium levels.
4. Certain Medications
Some medications, such as diuretics, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and antibiotics, can interfere with magnesium absorption or increase its excretion.
5. Digestive Disorders
Conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) can impair the body’s ability to absorb magnesium from food.
6. Aging
As we age, our bodies become less efficient at absorbing magnesium, and kidney function may decline, leading to increased magnesium loss through urine.
Top Sources of Magnesium
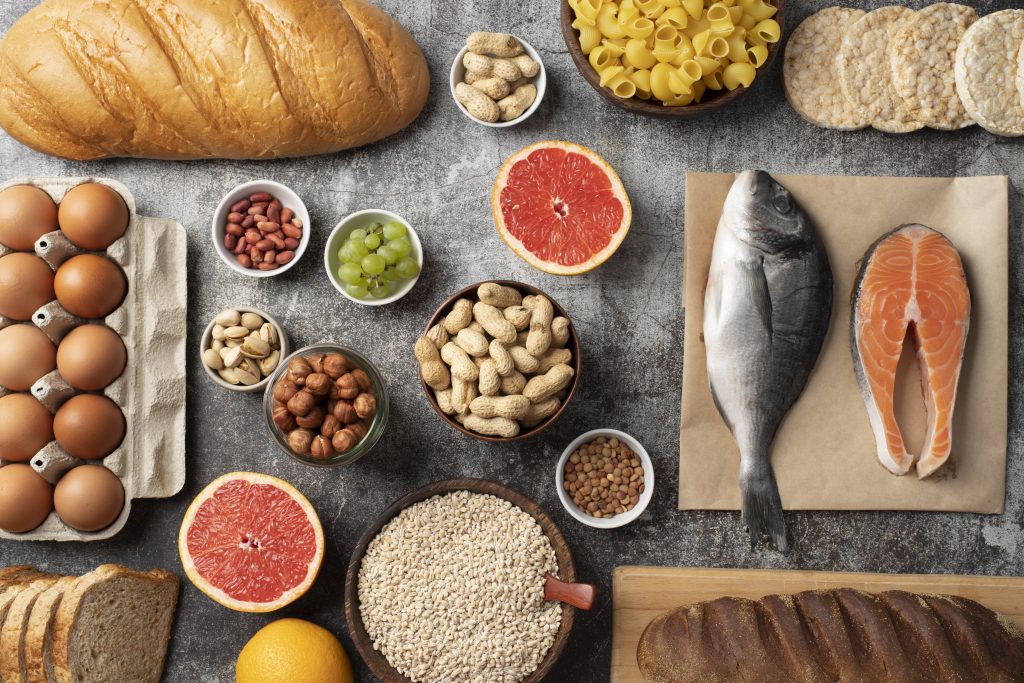

The good news is that magnesium is found in a wide variety of foods. Here are some of the best sources to include in your diet:
1. Leafy Greens
Spinach, kale, Swiss chard, and other leafy greens are excellent sources of magnesium. Just one cup of cooked spinach provides about 40% of your daily magnesium needs.
2. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds are not only delicious but also packed with magnesium. A handful of almonds can provide around 20% of your daily requirement.
3. Whole Grains
Quinoa, brown rice, oats, and whole wheat are rich in magnesium. Opt for whole grains over refined ones to maximize your intake.
4. Legumes
Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas are great plant-based sources of magnesium. They’re also high in fiber and protein, making them a nutritious addition to any meal.
5. Dark Chocolate
Yes, you read that right! Dark chocolate (with at least 70% cocoa) is a tasty source of magnesium. Just be mindful of portion sizes, as it’s also calorie-dense.
6. Fish
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and halibut are not only rich in omega-3 fatty acids but also provide a good amount of magnesium.
7. Supplements
If you struggle to get enough magnesium from food alone, supplements can be a helpful option. Magnesium citrate, glycinate, and oxide are popular forms, but it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
How Much Magnesium Do You Need?
The recommended daily intake of magnesium varies by age and gender:
- Adult men: 400–420 mg per day
- Adult women: 310–320 mg per day
- Pregnant women: 350–360 mg per day
Magnesium is a true unsung hero when it comes to maintaining optimal health. From supporting your heart and brain to improving sleep and muscle function, this essential mineral plays a role in nearly every aspect of your well-being.
By understanding the causes of deficiency and incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet, you can ensure your body gets the nutrients it needs to thrive.